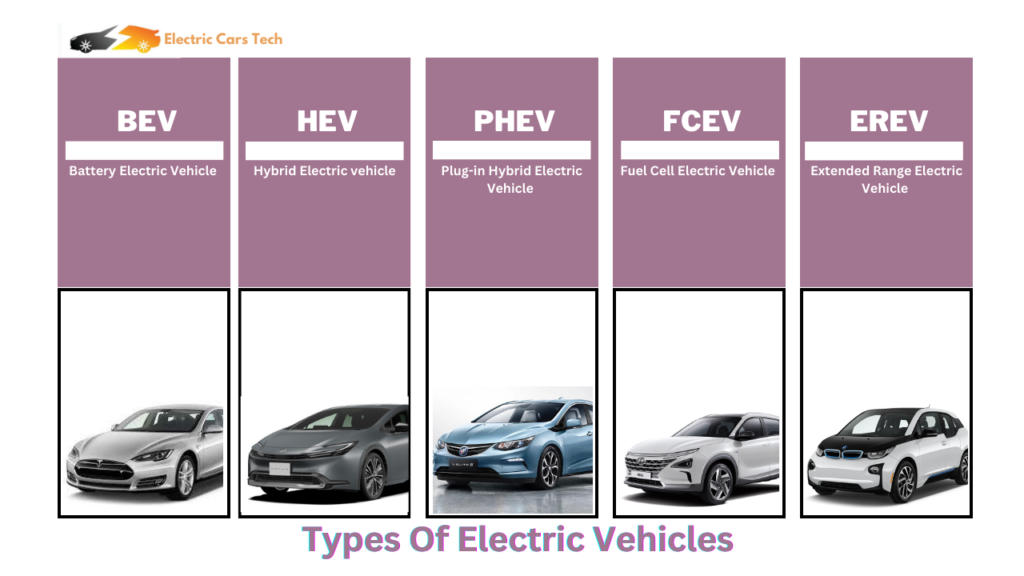
There are following types of electric vehicles available:
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
BEVs are also known as All-Electric Vehicles (AEV). These vehicles are powered entirely by rechargeable batteries and have no internal combustion engine. Their motors are fully powered by electricity. The enormous battery pack that houses the electricity needed to power the car may be charged by hooking it into the power grid. One or more electric motors are then powered by the fully charged battery pack to drive the electric vehicle.
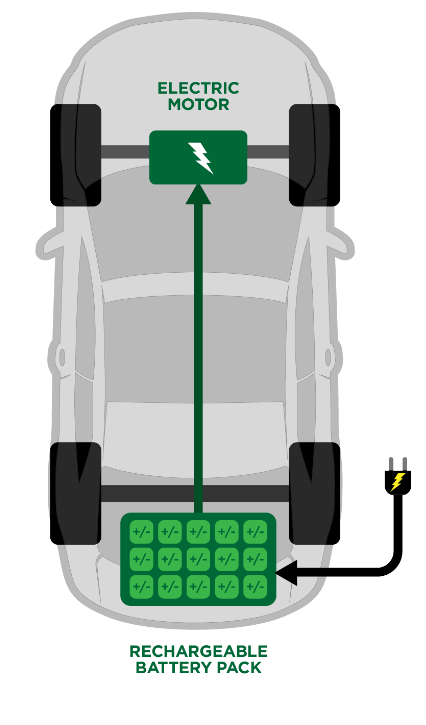
Main Components:
Battery pack
Electric motor
Power electronics
Charging port
Working Principle:
Fully electric vehicles known as Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) store and use electricity through rechargeable battery packs to power their electric motors. The battery pack, which stores the electricity used to power the vehicle, is the most important part of a BEV. The majority of battery packs are composed of lithium-ion cells, and the vehicle they are used in determines their capacity and range.
The vehicle’s wheels are propelled by the electric motor, which transforms electrical energy from the battery pack into mechanical energy.To ensure effective functioning, power electronics are employed to control the electricity flow between the battery pack and the electric motor. BEVs function by using the battery pack’s stored energy to drive the electric motor, which turns the car’s wheels. The car must be hooked into a wall outlet or charging station when the battery pack runs out of juice.
Examples of BEVs: Tesla Model S, Nissan Leaf, Chevrolet Bolt
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV):
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV): HEVs are also known as series hybrid or parallel hybrid. These vehicles combine an electric motor with a gasoline or diesel engine. The electric motor provides additional power to the engine, helping to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Fuel powers the engine, while batteries provide electricity for the motor. Both the engine and the electric motor turn the transmission at the same time. Wheels are then propelled by this.
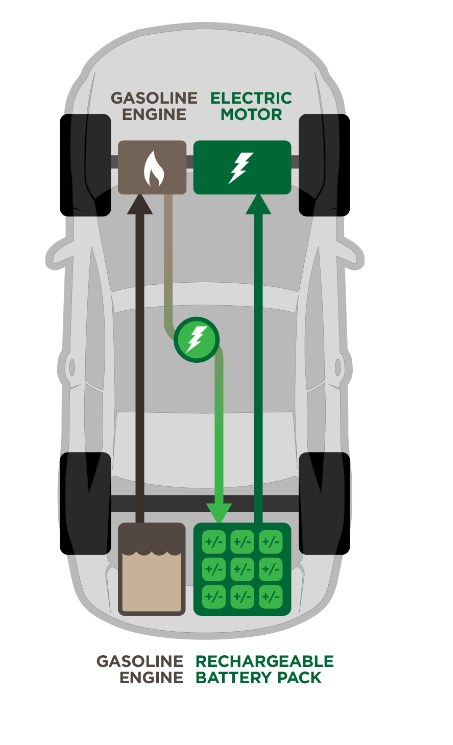
Main Components:
Battery pack
Electric motor
Internal combustion engine
Transmission
Power electronics
Working Principle:
- The working principle of HEVs can be explained in the following steps:
- When the battery pack begins to deplete, the ICE is turned on to produce electricity to power the electric motor or recharge the battery pack.
- Depending on the vehicle’s design, the ICE can be fueled by gasoline, diesel, or other fuels.
- HEVs can also capture energy lost during braking and use regenerative braking to recharge the battery pack.
- Depending on the input from the driver and the driving environment, the car can function in a number of modes, including electric, hybrid, and ICE modes.
- HEVs use a transmission system that enables the vehicle’s ICE and electric motor to operate in tandem to provide power.
Examples of HEVs: Toyota Prius, Honda Insight, Ford Fusion Hybrid
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
The PHEVs are also known as series hybrids. These vehicles are similar to HEVs, but with larger battery packs that can be charged from an external power source. This allows them to run on electric power alone for a limited distance before switching over to their internal combustion engine. You have a choice of two types of fuels: conventional fuel (like gasoline) and alternative fuel (such as bio-diesel). A battery pack that can be recharged can also power it. The battery can be externally charged.
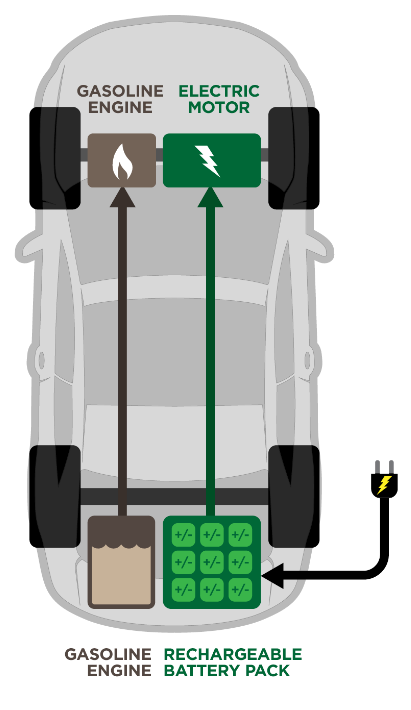
Main Components:
Battery pack
Electric motor
Internal combustion engine
Transmission
Power electronics
Charging port
Working Principle:
The working principle of PHEVs can be explained in the following steps:
• The car can be started using electricity, using the battery pack to turn the wheels.
• When the battery pack begins to deplete, the ICE is turned on to produce electricity to power the electric motor or recharge the battery pack.
Depending on the vehicle’s architecture, the ICE may be fueled by gasoline, diesel, or other fuels.
• PHEVs can also capture energy lost during braking and use regenerative braking to recharge the battery pack.
• Because the vehicle can be charged from an external power source, usually an electrical outlet, it can operate in all-electric mode for longer distances.
- PHEVs can operate in a variety of modes, including electric mode, hybrid mode, and ICE mode, depending on the driver’s input and the vehicle’s operating conditions.
Examples of PHEVs: Chevy Volt, Ford C-Max Energi, BMW i3 Rex
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) use fuel cell technology to generate electricity to power their electric motors. The working principle of FCEVs involves a series of chemical reactions that occur in the fuel cell stack to produce electricity.
Main Components:
Fuel cell stack
Hydrogen storage tank
Electric motor
Power electronics
Working Principle:
- The following steps can be used to describe how FCEVs operate:
- Hydrogen is taken into the fuel cell stack and electrolyzed to separate it into protons and electrons.
- In a fuel cell stack, protons are drawn via a membrane while electrons are compelled to move through an external circuit to produce power.
- On the other side of the membrane, the electrons and protons are subsequently reunited, and the sole byproduct is water vapour, which is created when they react with oxygen from the surrounding air.
- The electricity generated by the fuel cell stack is used to power the electric motor, which turns the wheels of the vehicle.
- Any excess electricity can be stored in a small battery pack or used to power other vehicle systems.
- When the hydrogen in the tank runs low, the vehicle must be refueled at a hydrogen fueling station.
Examples of Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) : Toyota Mirai, Hyundai Nexo, and Honda Clarity Fuel Cell.
Extended-Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs)
These cars resemble PHEVs but have a bigger battery that can extend the all-electric driving range. A gasoline or diesel engine produces electricity to power the electric motor when the battery is empty.
Main Components:
Battery pack
Electric motor
Internal combustion engine
Generator
Power electronics
Charging port
Working Principle:
The working principle of EREVs can be explained in the following steps:
- The vehicle starts in electric mode, with the electric motor drawing power from the battery pack to turn the wheels.
- When the battery pack starts to run low, the ICE is activated to generate electricity to recharge the battery pack.
- The ICE can be powered by gasoline, diesel, or other fuels, depending on the vehicle’s design.
- The electricity generated by the ICE is used to recharge the battery pack, which can then be used to power the electric motor again.
- EREVs can also use regenerative braking to recharge the battery pack, capturing energy that would otherwise be lost during braking.
- The vehicle can switch between electric mode and generator mode automatically as needed, without any input from the driver.
Examples of EREVs: Chevrolet Volt, BMW i3 REx
Read About: The Ultimate Guide and Basics of EV Charging
“The Future of Transportation: Why Electric Cars are the Way Forward?”
Interested in stock market / cryptocurrency visit :Ewebblogger.com

ElectricCarsTech is a dedicated blogger with a passion for electric vehicles (EVs). Committed to bringing the latest trends, updates, and insights from the EV world, this blog serves as a hub for enthusiasts and curious minds alike. Stay charged with ElectricCarsTech and drive into the future of mobility with us.