Unveil the breakthroughs in ‘Electric Car Safety Features’ with our detailed article. Learn about their innovative structural designs, advanced driver-assistance systems, and cutting-edge cybersecurity that make EVs a safe, smart choice for modern transportation
As the global push towards a cleaner, more sustainable environment intensifies, electric cars are at the forefront of this transition, heralding a new era in the automotive industry. Not only do these vehicles offer the promise of zero emissions, but they also boast an array of innovative safety features that set them apart from conventional cars. This article provides a detailed look into the unique safety features of electric cars, giving you a broader perspective on why they represent not only a sustainable choice, but also a secure one.
List: Must Have Electric Car Safety Features.
1. Structurally Sound Designs
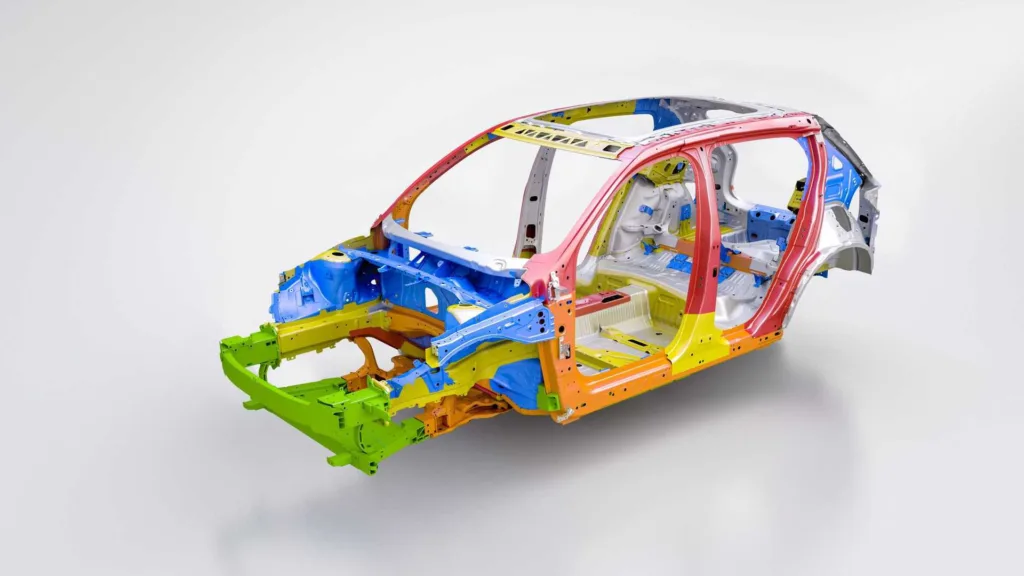
Electric vehicles (EVs) often carry a different structural design compared to traditional combustion engine cars. Unlike traditional cars with large engine blocks, EVs utilize compact electric motors, allowing for increased crumple zones. These specially designed areas absorb the energy during a collision, protecting passengers by reducing the force they experience. Additionally, heavy batteries in EVs are strategically placed under the floor. This lowers the vehicle’s center of gravity, enhancing stability, and significantly decreasing rollover risks.
By redistributing the weight evenly, this design also improves traction and control, ensuring safer handling. In essence, the unique structural design of EVs not only optimizes space but also elevates safety standards, making them a compelling choice for the safety-conscious driver.

2. Advanced Battery Management System
The lithium-ion batteries used in electric cars have sparked discussions about potential fire hazards. However, top electric car manufacturers invest heavily in advanced safety systems to ensure battery protection. These systems include robust battery enclosures, automatic disconnect features in case of a collision, and advanced cooling systems to prevent overheating. Some manufacturers have gone a step further to use non-flammable electrolytes in their batteries to enhance safety.
The management systems incorporated into electric vehicle (EV) batteries, known as Battery Management Systems (BMS), serve to oversee and optimize the battery’s function, guaranteeing its safe and efficient operation. The BMS utilizes an array of sensors that continuously track parameters such as the battery’s charge status, temperature, and voltage. These sensors then modulate the system to ensure optimal performance. By doing so, the BMS effectively mitigates risks associated with overcharging, excessive heat, and other potential complications, thereby ensuring both enhanced battery performance and safety.
3. Regenerative Braking
Among the numerous advancements electric vehicles (EVs) bring to the table, regenerative braking stands out as a truly transformative safety feature. Unavailable in traditional combustion-engine vehicles, this feature is not only a marvel of energy conservation but also a potent ally in ensuring vehicular safety.
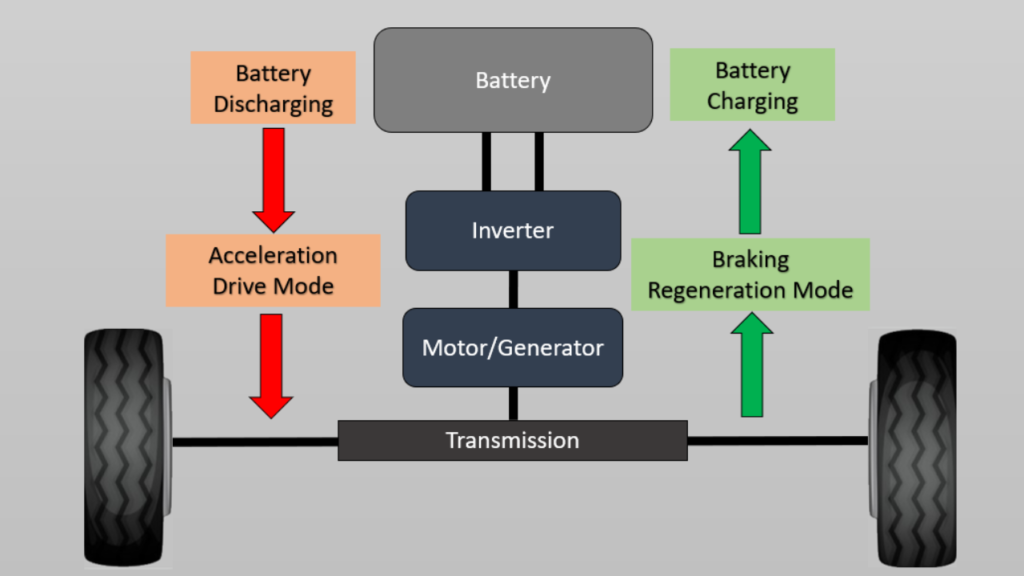
At its core, regenerative braking is an energy recovery mechanism that slows down a vehicle by converting its kinetic energy into a form that can be used immediately or stored until needed. This transformation takes place during periods of deceleration, where instead of losing energy as heat through friction (as happens in conventional braking), the electric motor operates in reverse, generating electricity that recharges the battery.
One of the key safety benefits of this system is the reduced wear and tear on the braking system. As the electric motor takes on much of the deceleration, the vehicle’s traditional brakes are used less frequently, resulting in a longer lifespan and less maintenance. This extends the intervals between necessary brake replacements and services, reducing the chances of brake failure and enhancing overall vehicle reliability.
Furthermore, regenerative braking offers an added safety feature during emergencies. The system initiates the moment the driver’s foot lifts off the accelerator, slowing down the car without the need to engage the traditional brakes. This feature provides the driver with an additional layer of control and response time in unforeseen circumstances, thus ensuring safer driving.
4. Quiet Yet Safe
One of the most noticeable characteristics of an electric car is its quiet operation, thanks to the absence of a roaring engine. While this brings a serene driving experience, it can potentially pose a risk to pedestrians who might not hear the vehicle approaching. To mitigate this, many electric vehicles now come with acoustic vehicle alerting systems (AVAS) that emit artificial sounds, alerting pedestrians of their presence.
5. Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
As we hurtle towards a future increasingly defined by technological innovation, the safety features of electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly evolving and setting new standards in vehicular safety. A prime example of this evolution is the incorporation of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) in many modern electric cars.
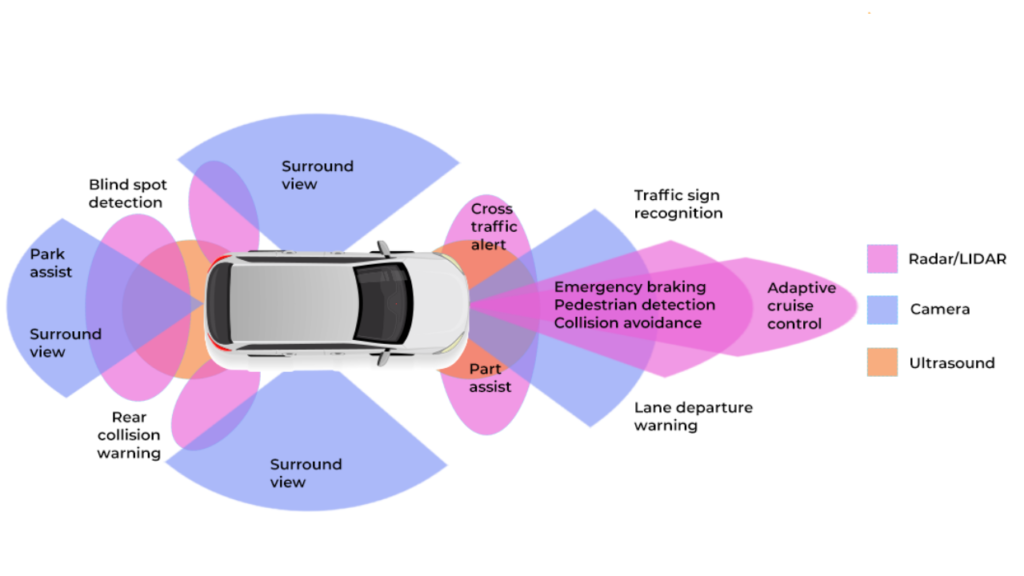
ADAS, in essence, is a set of systems and subsystems that utilize advanced technologies to automate, adapt, and enhance vehicle systems for safety and improved driving. The benefits are multifold: they aid drivers in difficult or monotonous driving situations, reduce human errors, and, most importantly, significantly decrease the risk of accidents.
Among the array of features ADAS offer, some particularly noteworthy ones include automatic emergency braking, blind-spot detection, lane departure warnings, and adaptive cruise control. Automatic emergency braking systems help to prevent collisions by applying the brakes when a potential impact is detected.
Blind-spot detection notifies the driver of vehicles or obstacles in blind spots that are not visible in the rearview mirror. Lane departure warnings alert the driver when the vehicle begins to move out of its lane unintentionally. Adaptive cruise control maintains a safe distance from the vehicle ahead by automatically adjusting speed.
Two pioneering examples of comprehensive ADAS in electric vehicles are Tesla’s Autopilot and Nissan’s ProPilot Assist. Tesla’s Autopilot offers features like self-parking, adaptive cruise control, and lane-centering. Nissan’s ProPilot Assist provides similar features, demonstrating how ADAS can contribute to safer roads and reduce the likelihood of accidents.
6. Post-Collision Safety
Electric vehicles (EVs) place significant emphasis on safety, not just during everyday operations, but even post-collision. In the unfortunate event of a severe crash, EVs are equipped with features designed to protect both the vehicle’s occupants and first responders from potential electrical hazards. One such feature is the automatic battery disconnect. Upon sensing a collision, this system cuts off the battery’s connection, preventing any further discharge of electricity.
Similarly, the high-voltage components are immediately deactivated, mitigating the risk of electrical shocks. This advanced approach to safety in electric cars is testament to the comprehensive protective measures embedded in their design, ensuring maximum safety even in the aftermath of an accident.
7. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Electric vehicles (EVs) have transcended the boundaries of traditional automotives by embracing the power of over-the-air (OTA) updates. A pivotal safety feature, OTA updates are a remarkable way to address software issues, fix bugs, upgrade systems, and even enhance safety features, all in real-time.
Unlike conventional cars that might necessitate a recall or a service center visit to rectify issues, EVs bypass this time-consuming process. By leveraging wireless communication technology, these vehicles can receive and install software updates remotely. This transformative feature ensures that the vehicle is always up-to-date with the latest firmware, and any identified vulnerabilities are swiftly patched.
OTA updates also provide a means to roll out new features or improvements to existing functionalities. For instance, a manufacturer could enhance an existing safety feature like advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) via an OTA update, further bolstering the safety of the vehicle.
8. Pedestrian Safety Systems
In addition to the aforementioned acoustic vehicle alerting systems (AVAS), some electric vehicles now incorporate active pedestrian safety systems. These can detect pedestrians in the path of the vehicle and either warn the driver or automatically apply the brakes to prevent an accident. This feature, often paired with cyclist detection, shows the commitment of EV manufacturers to road safety for all users, not just drivers and passengers.
9. Advanced Airbag Systems
The design flexibility that electric vehicles offer, due to the lack of a traditional internal combustion engine, provides room for manufacturers to innovate when it comes to passenger protection. One such innovation comes in the form of advanced airbag systems. In addition to the standard front and side airbags found in most vehicles, some electric cars now feature new airbag locations, such as roof airbags, front center airbags, and even external airbags designed to protect pedestrians.
10. Cybersecurity
With the surge in popularity of electric vehicles (EVs), there is a corresponding rise in the demand for advanced cybersecurity measures. Modern EVs, with their connected systems and intricate digital interfaces, are essentially ‘computers on wheels’. This makes them potential targets for cybercriminals, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity technologies.
Cybersecurity in EVs is a combination of hardware and software systems designed to prevent unauthorized access to the vehicle’s data and control systems. This shields the vehicle from cyber threats, protects user data, and ensures the integrity of its various functionalities.
One critical area where cybersecurity plays a pivotal role is in the transactions between EVs and smart charging stations. As EVs connect to these stations for charging, they exchange data regarding battery status, charging rates, billing information, and more. Without strong cybersecurity measures, this data exchange could be vulnerable to hacking or unauthorized access.
Manufacturers are therefore investing heavily in securing these transactions, using techniques such as encryption and secure communication protocols. Additionally, regular software updates are deployed to ensure that the cybersecurity measures are up-to-date and capable of countering new threats.
11. Electric Vehicle Health Monitoring Systems
Lastly, and importantly, electric cars often include health monitoring systems. These smart systems continuously check the status of various components of the vehicle, including the battery, motor, and other essential parts. If an issue or potential issue is detected, the system will notify the driver, allowing for proactive maintenance and repairs. This not only prevents potential breakdowns but can also alert drivers to issues that, if left unattended, could create unsafe conditions. This real-time monitoring and reporting feature is yet another layer of safety offered by electric vehicles.
12. Collision Avoidance Systems
Even though it shares similarities with blind-spot detection, the Collision Avoidance System (CAS) in electric vehicles (EVs) serves a more proactive role in promoting safety on the road. Utilizing advanced sensor technology and machine learning algorithms, CAS not only keeps an eye on the surrounding vehicles but also constantly monitors the EV’s own speed.
In a situation where the CAS predicts a possible collision based on its data analysis, it promptly provides notifications or alerts to the driver. These alerts can potentially give the driver the precious seconds needed to take evasive action, thus averting a collision or significantly reducing its severity.
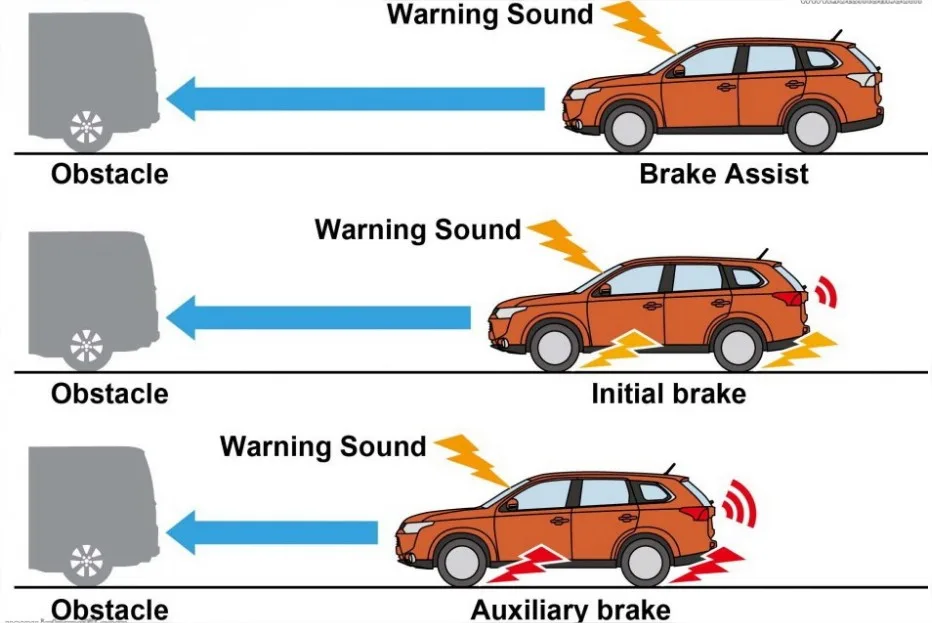
Moreover, in some sophisticated models, the CAS goes beyond providing alerts. It can autonomously take control of the vehicle to reduce speed, apply brakes, or even steer away from the potential danger when a collision is imminent. This ‘intervention’ by CAS proves invaluable, especially in situations where human reaction time might not be adequate.
By acting as a virtual co-pilot, the Collision Avoidance System is a critical safety feature in EVs.
13. Blind Spot Monitoring
The most common issue of passenger vehicles is remedied with blind spot monitoring solutions. With improved visibility, blind spot monitoring also alerts the driver when a vehicle is in their ‘blind spot’ to prevent collisions when changing lanes of highways, but also supports driving in all other environments.
14. Rearview Camera
The rearview camera was introduced to modern cars in place of a mirror to improve the visibility of pedestrians and cars behind the vehicle. For electric cars, OEMs have improved functionality by including 360-degree panoramic view from the car, which is also leveraged for autonomous driving capabilities.
15. Fire-safe Materials
Battery combustion is the main concern from a fire and safety perspective. OEMs are using flame retardant coatings and insulation, as well as cooling systems that regulate the temperature of the battery and prevent thermal runaway. Emergency shut-off switches are also in place to isolate the battery in the event of a fire.
Conclusion
The advent of electric vehicles has not only revolutionized transportation but also radically enhanced vehicular safety. These 15 salient safety features provide a comprehensive overview of the remarkable strides that have been made in the realm of electric vehicle safety. Ranging from structurally sound designs, advanced battery management systems, and regenerative braking, to highly innovative features such as over-the-air updates, pedestrian safety systems, and advanced vehicle health monitoring systems, these safety measures provide an unprecedented level of protection to drivers, passengers, and pedestrians alike.
The inclusion of advanced driver assistance systems, post-collision safety measures, and robust cybersecurity technology further underscores the commitment of electric vehicle manufacturers to prioritize safety. As we look to the future, we can anticipate that these safety features will continue to evolve and improve, making electric vehicles an ever safer, smarter, and more sustainable choice for transportation.
FAQs
1. How do the structural designs of electric vehicles enhance safety?
Electric vehicles benefit from design elements that enhance safety, such as the absence of a large engine block which allows for more crumple zones, and the underfloor placement of heavy batteries which lowers the vehicle’s center of gravity, reducing rollover risk and increasing stability.
2. How do electric vehicles ensure battery safety?
Electric vehicles utilize advanced battery management systems that monitor and manage battery function, preventing overcharging and overheating. Other safety measures include robust battery enclosures, automatic disconnect features, and advanced cooling systems. Some manufacturers even use non-flammable electrolytes in their batteries for added safety.
3. What are some unique safety features of electric vehicles?
Unique safety features of electric vehicles include regenerative braking, which conserves energy and reduces wear on the braking system, acoustic vehicle alerting systems (AVAS) for pedestrian safety, over-the-air (OTA) updates for real-time software improvements, and advanced vehicle health monitoring systems that provide proactive alerts for maintenance and repairs.
4. How do electric vehicles protect pedestrians?
Many electric vehicles now incorporate active pedestrian safety systems that can detect pedestrians in the vehicle’s path and either warn the driver or automatically apply the brakes. Additionally, AVAS systems emit artificial sounds to alert pedestrians of the vehicle’s presence.
5. How do electric vehicles ensure cybersecurity?
Electric vehicles employ advanced cybersecurity technology that includes software and hardware designed to prevent unauthorized access to data via vehicle systems, particularly important for transactions between EVs and smart charging units.

ElectricCarsTech is a dedicated blogger with a passion for electric vehicles (EVs). Committed to bringing the latest trends, updates, and insights from the EV world, this blog serves as a hub for enthusiasts and curious minds alike. Stay charged with ElectricCarsTech and drive into the future of mobility with us.

